Company Car Tax On Electric Cars
What's Covered
- Introduction
- Who Pays Company Car Tax?
- Switch From NEDC To WLTP CO2 Figures
- BIK Tax Bands For 2020-23 (Car Registered Before April 6 2020) NDEC
- BIK Company Car Tax Bands For 2020-23 (Car registered From April 6 2020) WLTP
- BIK Rate For Electric Vehicles (EVs)
- BIK Rate For Plug-In Hybrid Vehicles (PHEVs)
- How Benefit In Kind (BIK) Tax Is Calculated
- Vehicle Excise Duty (VED)
- Capital Allowances
- Summary
If there’s ever been a time for businesses to jump on the electric car bandwagon, now is that time.
Since 2020, company car tax (benefit in kind, or BIK) for electric cars has been lower than ever. Previously taxed at 16%, it dropped to 0% for 2020-21, then 1% for 2021-22, and it's now 2% for 2022-23.
If you’re looking for the full list of BIK rates for all possible CO2 emissions, see our post. If you're looking for a more general guide to how company car tax is calculated, see our company car tax explained post.
This explainer guide here specifically highlights the benefits of electric vehicles as company cars and how BiK rates are calculated.
Who Pays Company Car Tax?
You have to pay BIK tax if:
- You use a company car and were only given the option of a company car (not car allowance).
- You get a company car through a salary sacrifice car scheme.
- You were given the option of a company car or car allowance and the BIK tax is higher than the cash allowance.
- You have taken out a limited company car lease (or other finance option).
You do not have to pay BIK tax if:
- You're self employed with a business car lease.
- You have the choice between a company car or car allowance, and the cash allowance value is higher than BIK tax.
Switch From NEDC To WLTP CO2 Figures
Previously, CO2 emissions were calculated using an official NDEC.
However, in 2018, the Government announced that from 6th April 2020, the CO2 figures used to calculate BIK rates will switch from the outdated NEDC test to the WLTP.
The WLTP procedure was introduced in EU countries in 2017 and has been successful in measuring pollutant emissions and fuel efficiency more accurately.
As a result of the switch, the Government has produced two Bik tax tables - one for drivers with cars registered before the 6th April 2020 and one for those who are planning to register a car after this date.
From 2022 onwards, the figures are the same for pre and post-April 2020 registered cars, so this mattered more before this date.
BIK Tax Bands For 2020-23 (Car Registered Before April 6 2020) NDEC
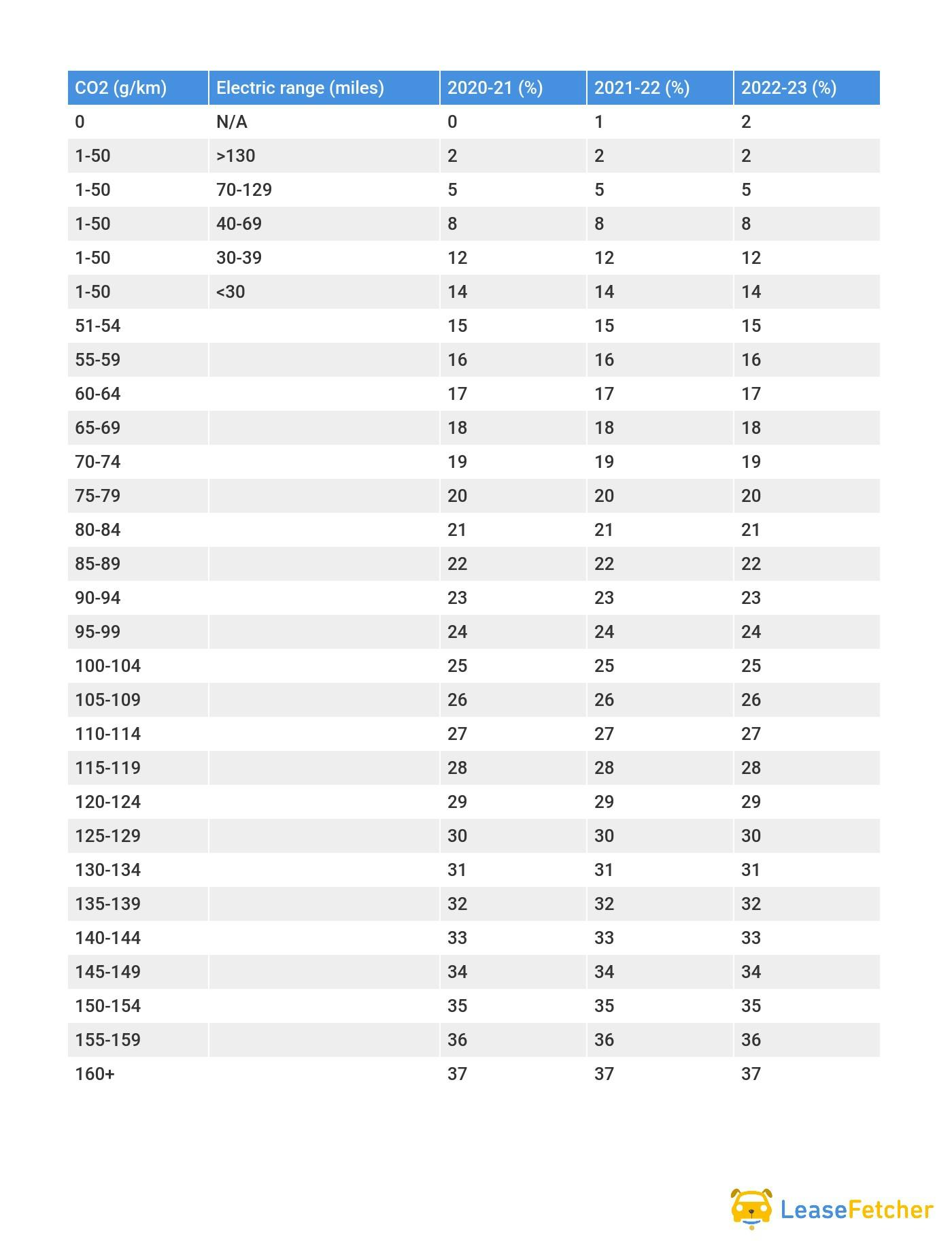
*add 4% up to a maximum of 37% for diesel cars that are not certified to the Real Driving Emissions 2 (RDE2) standard. Diesel plug-in hybrids are exempt from the 4% surcharge as they are classed as alternative fuel vehicles.
BIK Company Car Tax Bands For 2020-23 (Car registered From April 6 2020) WLTP
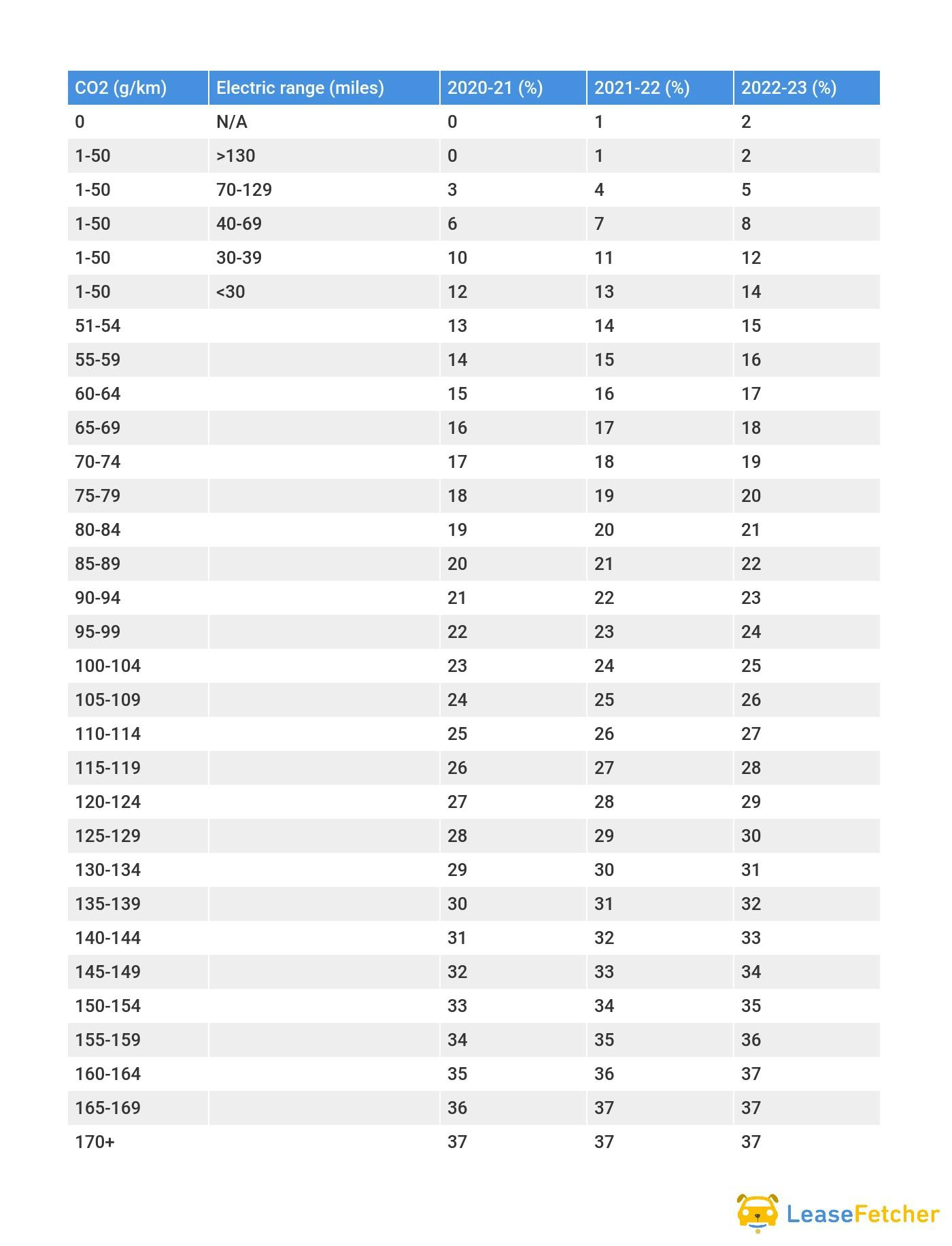
*add 4% up to a maximum of 37% for diesel cars that are not certified to the Real Driving Emissions 2 (RDE2) standard. Diesel plug-in hybrids are exempt from the 4% surcharge as they are classed as alternative fuel vehicles.
As you can see from the two tables, there are huge savings benefits available to those who choose a zero emissions electric car or a lower CO2 emissions vehicle like a plug-in hybrid.
BIK Rate For Electric Vehicles (EVs)
For 2022-23, EV company car drivers will pay just 2% BIK tax.
For cars that emit 1-50g of CO2 and which have 130 miles or more of electric range, the BIK tax rate is also 2%. It goes up to 5% for the same carbon emissions but for 70-129 miles of electric range.
From 2022 onwards, you'll pay the same BIK tax for cars registered before and after April 2020.
BIK Rate For Plug-In Hybrid Vehicles (PHEVs)
The total amount of company car tax that a plug-in hybrid (PHEV) has to pay depends on how far the vehicle can be driven with zero emissions, rather than its actual CO2 emissions.
As long as the car produces below 50g CO2/km, the following rates apply:
- Capable of more than 130 electric miles: 2%
- 70-129 electric miles: 5%
- 40-69 electric miles: 8%
- 30-39 electric miles: 12%
- Less than 30 electric miles: 14%
If the PHEV produces more than 50g CO2/km, even if it does more than 30 electric miles, it'll be charged:
- 15% tax for 51-54g CO2/km
- 16% for 55-59g CO2/km
- 17% for 60-64g CO2/km
- 18% for 65-69g CO2/km
And so on.
How Benefit In Kind (BIK) Tax Is Calculated
To manually calculate the BiK tax on your EV, you’ll need a calculator and a few important figures:
- P11D Value - Original list price of your car (with added extras but without registration/tax fees)
- CO2 Emission tax band (%)
- Your Personal Income Tax Bracket
To calculate your company car tax, you need to use the following formula:
P11D Value x CO2 Emissions Tax Band Percentage x Personal Rate = Annual Company Car Tax.
We'll take a look at "Andy". Andy's company have chosen a Nissan Leaf as the company car. It produces no emissions.
They purchased the car in 2020, when it cost £30,135. This P11D value will be used throughout the years, rather than adjusting for the changing price of the model.
Andy is a Scottish resident and earns £30,000 a year. He falls under the Intermediate Personal Income Tax bracket of 21%.
- P11D value - £30,135
- CO2 Emissions - 0 g/km
- CO2 Emission tax band - 2%
In 2022/23 Andy would be paying:
(£30,135 x 2%) = £602.70 x 21% = £126.57 per year or £10.55 per month.
Vehicle Excise Duty (VED)
More casually referred to as road tax, Vehicle Excise Duty (VED) is calculated based on your car’s CO2 emissions, list price (P11D value), and the year it was registered.
Since the 31st March 2017, most electric cars have been exempt from paying road tax. The Government initiative has aimed to support drivers who promote clean and sustainable driving.
For PHEVs, you’ll pay in the region of £10-115 for your first year depending on the vehicle’s CO2 emissions and then £155 for the subsequent years.
If you have a car worth over £40,000 (not EVs), it'll fall into a "Premium Rate" category. You can add £335 on to to prices listed below, payable for for the first five years after the car is registered.
Top tip - all cars that emit less than 75g/km CO2 will pay significantly less road tax in the first year which will definitely go down well with the boss.
| CO2 Emissions (g/km) | First Year Rate | Standard (Second Year) Rate |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | £0 | £0 |
| 1-50 | £10 | £155 |
| 76-90 | £115 | £155 |
| 91-100 | £140 | £155 |
| 101-110 | £160 | £155 |
| 111-130 | £180 | £155 |
| 131-150 | £220 | £155 |
| 151-170 | £555 | £155 |
| 171-190 | £895 | £155 |
| 191-225 | £1,345 | £155 |
| 226-255 | £1,910 | £155 |
| Over 255 | £2,245 | £155 |
Capital Allowances
You can claim capital allowances for cars you have bought for business use. This enables you to deduct part of the cost you paid for the car from your profits before you pay tax.
The desired criteria for a car is:
- It must be suitable for private use.
- Most people use it privately.
- It must not be built for transporting goods.
The rate that you can claim for capital allowance depends on when you bought the vehicle and of course, the CO2 emissions of the car.
Cars newly bought between April 2015 and April 2018 are eligible to deduct the full value of the car if CO2 emissions are 75g/km or less.
For cars bought after the 31st April 2018, you’re only eligible for a full deduction if the car emits 50g/km or less CO2.
Summary
In a bid to electrify our roads, company car tax on electric cars is cheaper than it has ever been before, and businesses can enjoy the low rates for years to come.
If you're interested in how you can reduce the cost to lease a car for your business, check our car lease tax deduction post. Or if you're leasing a van for business, see our company van tax post.
Ready to take the plunge and take out a business car leasing deal? Check out our electric car lease deals and hybrid lease deals. For inspiration, you can browse our round up of the best electric cars and best hybrid cars.
For more on business contract hire in general, please see our "how does business car leasing work?" guide!
What's Covered
- Introduction
- Who Pays Company Car Tax?
- Switch From NEDC To WLTP CO2 Figures
- BIK Tax Bands For 2020-23 (Car Registered Before April 6 2020) NDEC
- BIK Company Car Tax Bands For 2020-23 (Car registered From April 6 2020) WLTP
- BIK Rate For Electric Vehicles (EVs)
- BIK Rate For Plug-In Hybrid Vehicles (PHEVs)
- How Benefit In Kind (BIK) Tax Is Calculated
- Vehicle Excise Duty (VED)
- Capital Allowances
- Summary


